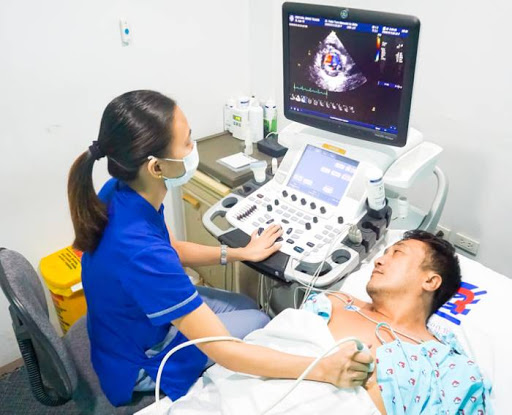
Invasive Cardiology
Invasive cardiology uses open or minimally-invasive surgery to identify or treat structural or electrical abnormalities within the heart structure.
Common types of invasive cardiology:
- Angioplasty: When plaque clogs your arteries, it becomes difficult for blood to flow normally. Angioplasty inserts a tiny balloon into your clogged vein and pushes plaque against the walls, allowing for increased blood flow.
- Stenting: Stenting is usually done in conjunction with angioplasty. A cardiac stent is a small metal coil which permanently holds a clogged vein open.
Non-Invasive Cardiology
Non-invasive cardiology identifies heart problems without using any needles, fluids, or other instruments which are inserted into the body.
Non-invasive cardiologists utilize techniques such as:
- Nuclear cardiology: A non-invasive study of cardiovascular disorders by means of various types of imaging which may use radioactive elements.
- Echocardiography: The usage of ultrasound waves to create images of the heart and surrounding structures in order to identify how well the heart pumps blood, infections, and structural abnormalities.
- Cardiac electrophysiology: Study and testing of the electrical currents which generate heartbeats.
- Stress tests: Stress testing usually involves exercise which is monitored by your cardiologist. These exercises provide your cardiologist information about how your heart performs under physical stress.
- Heart monitors: Heart monitors may also be called a Holter monitor or cardiac event recorder. Heart monitors are essentially tape recorders for your heart’s electrical activity over a set amount of time.
- CT scans: CT scans produce images which your cardiologist can examine for heart disease and atherosclerosis.
Once your specialist has identified risk factors or existing conditions, they may recommend medication and lifestyle changes to improve your heart’s health.
Interventional Cardiology
Interventional cardiology is a non-surgical option which uses a catheter – a small, flexible tube – to repair damaged or weakened vessels, narrowed arteries, or other affected parts of the heart structure.
Common conditions treated by interventional cardiology:
- Coronary artery disease: A narrowing of the arteries which supply the heart muscle with blood and oxygen.
- Heart valve disease: Occurs when the valves which control blood flow into the heart’s chambers are not working correctly.
- Peripheral vascular disease: Your heart can also be affected by clogged or hardened veins and arteries which are in other parts of your body.